Designed for individuals seeking guidance on proper nutrition and diet advice, our tips will help you create a balanced meal plan that promotes optimal well-being.
By incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet and avoiding triggers that exacerbate inflammation, you can enhance your body’s natural ability to heal and protect against various health conditions. Discover practical strategies and nutritional guidelines that will empower you to make informed choices, paving the way for a healthier, more vibrant life.
Understanding Inflammation

What is Inflammation?
The body’s immune system triggers inflammation as a natural response to safeguard itself from harmful stimuli like pathogens, toxins, or injuries. This reaction typically manifests as redness, swelling, warmth, and pain in the affected area. Although acute inflammation is vital for the healing process, prolonged or chronic inflammation can adversely impact your health.
The Link Between Inflammation and Health
Chronic inflammation is associated with various health issues, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, autoimmune disorders, and even cancer. Its contribution to the development and progression of these conditions lies in the gradual damage it inflicts on tissues and organs. Recognizing the connection between inflammation and health is essential for embracing a preventive approach to overall well-being.
Introduction to Anti-Inflammatory Diet
What is an Anti-inflammatory Diet?
An anti-inflammatory diet aims to reduce chronic inflammation in the body by emphasizing foods that have anti-inflammatory properties. By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods and avoiding or minimizing processed and refined ingredients, an anti-inflammatory diet can help maintain a healthy balance within the body’s inflammatory response system.
Benefits of Following an Anti-inflammatory Diet
There are numerous benefits to incorporating an anti-inflammatory diet into your lifestyle. Research suggests that it may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Additionally, it can support weight management, improve digestion, enhance immune function, and promote overall well-being.
Key Principles of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet

Consume A Variety of Whole Foods
A key principle of an anti-inflammatory diet is consuming a wide range of whole foods. This includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, nuts, and seeds. These nutrient-dense foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which can help combat inflammation and support optimal health.
Focus On Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables, especially those high in antioxidants, are essential components of an anti-inflammatory diet. Berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cabbage are particularly beneficial due to their high content of anti-inflammatory compounds such as flavonoids and phytochemicals.
Choose Healthy Fats
Including healthy fats in your diet is essential for reducing inflammation. Opt for sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel) and walnuts. Other healthy fats include avocados, olive oil, and nuts, which provide monounsaturated fats that are known to have anti-inflammatory properties.
Opt for Lean Protein Sources

Protein is necessary for tissue repair and overall growth and development. When selecting protein sources, choose lean options such as skinless poultry, fish, legumes, and tofu. These options are lower in saturated fats and can help reduce inflammation compared to processed or fatty meats.
Minimize Processed and Refined Foods
Processed and refined foods, such as sugary snacks, white bread, and fast foods, can trigger inflammation in the body. These foods are often high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives, which can contribute to chronic inflammation. Minimizing their intake is crucial for maintaining an anti-inflammatory diet.
Reduce or Eliminate Sugary Foods and Beverages
High sugar intake has been linked to various health issues, including inflammation. Refined sugars can trigger an inflammatory response in the body, leading to a cascade of negative health effects. Opt for natural sweeteners like honey or consume whole fruits as a healthier alternative.
Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can increase inflammation within the body. While moderate alcohol intake can have some health benefits, it is crucial to limit your consumption. Moderation, in this case, means one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
Stay Hydrated

Proper hydration is essential for overall health and supports the body’s natural detoxification processes. Drinking an adequate amount of water helps flush out toxins and waste products, preventing inflammation. Aim for at least eight cups (64 ounces) of water per day.
Use Herbs and Spices
Herbs and spices not only add flavor to your meals but also offer anti-inflammatory properties. Turmeric, ginger, garlic, cinnamon, and rosemary are just a few examples of spices and herbs that have been shown to reduce inflammation within the body. Adding these ingredients to your dishes can enhance their anti-inflammatory benefits.
Moderate Portion Sizes
Maintaining appropriate portion sizes is vital for maintaining a balanced and healthy diet. Overeating can lead to weight gain and increase the risk of chronic inflammation. Be mindful of portion sizes and listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues to avoid overeating.
✅ Foods to Include in Your Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Berries and Other Colorful Fruits

Berries, such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, are rich in antioxidants and can help reduce inflammation. Other colorful fruits, such as oranges, cherries, and grapes, are also beneficial due to their high content of vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Leafy Greens and Cruciferous Vegetables

Leafy greens like kale, spinach, and Swiss chard, along with cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts, are packed with essential nutrients and anti-inflammatory compounds. These vegetables should be staples in an anti-inflammatory diet.
Tomatoes and Peppers

Tomatoes and bell peppers are rich sources of lycopene and vitamin C, both of which possess anti-inflammatory properties. Whether consumed raw or cooked, these vegetables can contribute to a balanced and nutritious anti-inflammatory diet.
Fatty Fish and Seafood

Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids. These healthy fats have potent anti-inflammatory effects and are beneficial for heart health as well. Including fatty fish and other seafood in your diet, a few times a week is recommended.
Nuts and Seeds

Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, are packed with heart-healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants. They can be easily incorporated into meals or consumed as snacks, providing anti-inflammatory benefits and promoting satiety.
Whole Grains

Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat contain higher amounts of fiber and nutrients compared to refined grains. These grains can help stabilize blood sugar levels, reduce inflammation, and improve overall digestion when consumed as part of an anti-inflammatory diet.
Legumes and Beans

As great sources of plant-based protein, legumes and beans, including lentils, chickpeas, and black beans, offer a variety of health benefits. They are rich in fiber and phytonutrients, which can contribute to reducing inflammation and promoting gut health.
Healthy Oils

Incorporating healthy oils, such as olive oil, avocado oil, and flaxseed oil, into your anti-inflammatory diet can provide beneficial monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These fats have been associated with reduced inflammation and improved heart health.
Turmeric and Ginger

Turmeric and ginger are potent anti-inflammatory spices known for their active compounds, curcumin, and gingerol, respectively. These spices can be used in cooking or added to beverages like tea and smoothies to harness their anti-inflammatory benefits.
Green Tea

Green tea is a rich source of antioxidants, particularly catechins, which have anti-inflammatory properties. Drinking green tea regularly can support optimal health and contribute to an anti-inflammatory diet.
❌ Foods to Avoid or Limit in Your Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Processed and Refined Sugars
Foods and beverages high in processed and refined sugars, such as sodas, candies, pastries, and sugary cereals, can contribute to inflammation in the body. These foods should be avoided or limited as part of an anti-inflammatory diet.
Trans Fats and Hydrogenated Oils
Trans fats and hydrogenated oils, commonly found in fried foods, baked goods, and certain margarines, have been linked to increased inflammation and a higher risk of chronic diseases. Minimizing or avoiding these unhealthy fats is crucial in maintaining an anti-inflammatory diet.
Processed Meats
Processed meats, including sausages, hot dogs, and deli meats, often contain high amounts of sodium, unhealthy fats, and preservatives. These ingredients can trigger inflammation and increase the risk of various health issues. Instead, opt for lean protein sources like poultry or fish.
Highly Processed Snacks and Desserts

Snack foods like chips, crackers, and cookies, as well as desserts like ice cream and cakes, are typically high in refined grains, unhealthy fats, sugars, and additives. These processed snacks and desserts can contribute to inflammation and should be limited or avoided.
Sugary Drinks
Sugary drinks, such as soda, fruit juices, energy drinks, and sweetened iced tea, can generate a rapid increase in blood sugar levels and contribute to chronic inflammation. Opt for water, herbal tea, or unsweetened beverages to support an anti-inflammatory diet.
Excessive Alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to inflammation, especially in the liver and digestive system. It is recommended to limit alcohol intake to moderate levels to minimize the impact on inflammation and overall health.
Refined Grains

Refined grains, like white bread, white rice, and many breakfast cereals, have undergone processing that removes the bran and germ, stripping away beneficial nutrients and fiber. Consuming these refined grains can contribute to inflammation, so choosing whole grains is preferable.
Artificial Additives and Preservatives
Foods and drinks containing artificial additives and preservatives can trigger inflammation and negatively impact overall health. It is essential to read labels and avoid products with artificial ingredients as much as possible in an anti-inflammatory diet.
Highly Caffeinated Beverages
Highly caffeinated beverages, such as energy drinks and excessive amounts of coffee, can elevate cortisol levels and lead to inflammation within the body. Moderating caffeine intake and opting for herbal tea or decaffeinated alternatives is recommended.
Excessive Sodium
While some sodium is necessary for the body’s proper functioning, excessive sodium intake can contribute to water retention and high blood pressure, leading to inflammation. Reducing the consumption of heavily salted foods and choosing low-sodium options is important in an anti-inflammatory diet.
Meal Planning and Preparation

Developing a Meal Plan
Creating a meal plan can help you stay on track with your anti-inflammatory diet. Plan your meals and snacks in advance, ensuring they include a variety of anti-inflammatory foods, and make a shopping list accordingly. This will help you make healthier choices and avoid impulse buying.
Healthy Cooking Methods
The way you cook your food can impact its anti-inflammatory properties. Opt for healthier cooking methods like baking, steaming, grilling, or sautéing instead of deep-frying or using excessive oils. These methods can help preserve the nutrients and minimize the formation of harmful compounds.
Prepping Meals and Snacks in Advance
Meal prepping is a useful practice for maintaining an anti-inflammatory diet. Set aside some time each week to prepare and portion your meals and snacks in advance. This will save you time and ensure that you have nutritious options readily available, reducing the temptation to rely on processed or unhealthy foods.
Listening To Your Body’s Hunger and Fullness Cues
Listening to your body’s hunger and fullness cues is crucial for maintaining a balanced and healthy diet. Eat when you are hungry and stop when you are satisfied, being mindful of portion sizes. This approach can prevent overeating and contribute to sustainable weight management.
Avoiding Emotional Eating
Emotional eating can lead to unhealthy food choices and disrupt the balance of an anti-inflammatory diet. Instead of using food as a coping mechanism, explore alternative ways to manage stress and emotions, such as engaging in physical activity, practicing mindfulness, or seeking support from loved ones.
Mindful Eating Practices
Practicing mindful eating involves paying full attention to the sensory experience of eating, including the taste, texture, and smell of food, as well as your body’s hunger and satiety signals. This approach promotes a healthier relationship with food, helps prevent overeating, and enhances the enjoyment of meals.

Supporting Your Anti-Inflammatory Diet with Lifestyle Changes
Getting Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for overall health and can support the anti-inflammatory effects of your diet. Engage in both cardiovascular exercises, like jogging or cycling, and strength training activities to promote optimal well-being and reduce inflammation.
Managing Stress Levels
Chronic stress can contribute to inflammation within the body. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in hobbies, spending time with loved ones, or seeking professional help if needed. Managing stress effectively can help support your anti-inflammatory diet.
Achieving Quality Sleep

Quality sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal health and reducing inflammation. Aim for seven to nine hours of sleep per night, establish a relaxing bedtime routine, and create a sleep-friendly environment to support restorative sleep patterns.
Quitting Smoking
Smoking is a known contributor to chronic inflammation and various health issues. Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to support your anti-inflammatory diet and improve overall health. Seek professional help and utilize support systems to increase your chances of success.
Reducing Exposure to Environmental Toxins
Exposure to environmental toxins, such as air pollution, household chemicals, and pesticides, can promote inflammation within the body. Minimize your exposure by using natural cleaning products, avoiding heavily polluted areas, and consuming organic produce whenever possible.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is beneficial for overall health and can help reduce inflammation. If you are overweight, losing even a moderate amount of weight can provide substantial health benefits and support your anti-inflammatory diet. Combine a balanced diet and regular physical activity to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Seeking Professional Guidance

Consulting a Registered Dietitian or Nutritionist
For personalized guidance and support, consider consulting a registered dietitian or nutritionist. These professionals can assess your nutritional needs, help you create a customized anti-inflammatory diet plan, and provide ongoing guidance and accountability.
Working with a Healthcare Professional
If you have specific health conditions or concerns, it is crucial to work closely with your healthcare professional. They can offer tailored advice and monitor your progress, ensuring your anti-inflammatory diet aligns with your overall health goals and any existing treatments or medications.
Understanding Individual Dietary Needs
Everyone’s dietary needs vary, and what works for one person may not work for another. Factors such as age, sex, activity level, and existing health conditions can influence dietary recommendations. Understanding your individual dietary needs and tailoring your anti-inflammatory diet accordingly is essential for long-term success.
Addressing Underlying Health Conditions or Food Allergies
Individuals with underlying health conditions or food allergies may require additional considerations when following an anti-inflammatory diet. It is essential to address any specific dietary restrictions or modifications necessary to manage these conditions safely. Consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
Tips for Long-Term Success

Gradual Changes Overtime
Making gradual changes to your diet and lifestyle is more sustainable than attempting major shifts all at once. Start by incorporating small modifications, such as adding more vegetables to your meals or replacing sugary drinks with water, and gradually build on these changes over time.
Finding Healthy Alternatives and Substitutions
Identify healthy alternatives and substitutions for your favorite foods that align with your anti-inflammatory diet. Explore creative ways to replace less nutritious ingredients with more nutrient-dense options. For example, replace white rice with cauliflower rice or opt for natural sweeteners like stevia instead of refined sugars.
Building a Sustainable and Enjoyable Eating Routine
Creating a sustainable and enjoyable eating routine is key to long-term success with an anti-inflammatory diet. Experiment with different recipes, flavors, and cooking techniques to keep your meals exciting. Involve family or friends in meal planning and preparation to foster a sense of enjoyment and shared commitment to healthy eating.
Educating Yourself About Nutrition

Take the time to educate yourself about nutrition and the science behind an anti-inflammatory diet. This knowledge can empower you to make informed food choices and understand how your diet impacts your overall health and well-being.
Staying Motivated and Accountable
Staying motivated and accountable is crucial for maintaining an anti-inflammatory diet in the long term. Set specific goals, track your progress, and celebrate milestones along the way. Consider involving a friend or family member for additional support and accountability.
Celebrating Small Victories
Acknowledge and celebrate the small victories throughout your anti-inflammatory journey. Whether it’s choosing a healthy meal option or resisting an unhealthy temptation, these small victories build momentum and reinforce positive habits.
Creating a Supportive Environment
Creating a supportive environment is essential for long-term success. Surround yourself with people who share similar health goals and encourage your commitment to an anti-inflammatory diet. Consider joining online communities, and support groups, or finding an accountability partner to help you stay motivated.
Adapting Your Diet to Different Situations
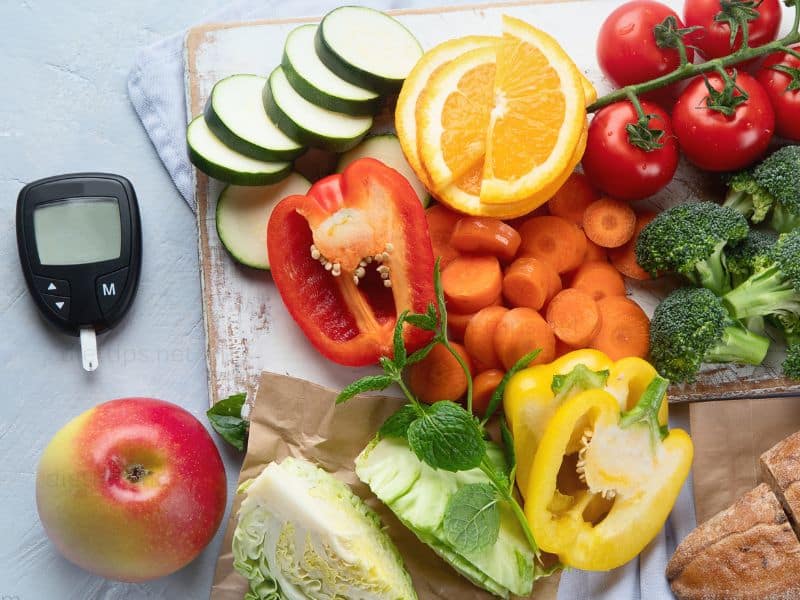
Being flexible and adaptable is important when following an anti-inflammatory diet. Understand that there may be situations where sticking strictly to your diet plan is challenging or not possible. In these situations, aim to make the best choices available and strive for balance rather than perfection.
Making it a Lifestyle, Not a Temporary Fix
Approach your anti-inflammatory diet as a long-term lifestyle change rather than a temporary fix. Embrace the principles of an anti-inflammatory diet as part of your overall approach to nutrition and well-being. Consistency and dedication to a healthy lifestyle will yield the best results.
Continuing To Learn and Explore New Foods
Stay curious and continue to learn about new foods and their potential health benefits. Experiment with different ingredients and recipes to keep your anti-inflammatory diet diverse and enjoyable. Don’t be afraid to step out of your comfort zone and explore new culinary experiences.
Conclusion
Embracing an anti-inflammatory diet is a proactive step toward improving your overall health and well-being. By incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, avoiding or limiting pro-inflammatory food choices, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, you can benefit from reduced inflammation, lower the risk of chronic diseases, and enhance your quality of life. Remember to consult with professionals and customize your diet according to your individual needs and goals, making it a sustainable and enjoyable lifestyle choice. With dedication and persistence, you can reap the rewards of a balanced and nutritious eating plan and live your best, inflammation-free life.